A motorcycle engine works the same way the car engine works. It has Pistons, a cylinder block and a head which consists of the valve train.
The engine generates power when the pistons move up and down rapidly in the cylinder block, this up and down motion is due to the combustion produced by the explosions of fuel and air mixture that is ignited by a spark.
Intake valves in the engine open and close to allow the air and fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber.
When the pistons move up and down, they turn the crankshaft and transforms the energy generated by pistons into rotatory motion.
Then the energy produced by the crankshaft is transmitted to the rear wheel via the transmission.
There Are Generally Three Classifications For Motorcycle Engines
- The capacity of the combustion chamber
- The number of Cylinders that engine has
- The number of strokes in their power cycle.
Capacity
The capacity of an engine is defined by the size of the combustion chamber of the motorcycle engine.
It starts from 50cc(cubic centimetres) and can go up to 2300cc. 50cc engines are usually found on small motorcycles(moped) or scooters that offer high mileage with less power, and they can go up to 40mph.
Cylinders
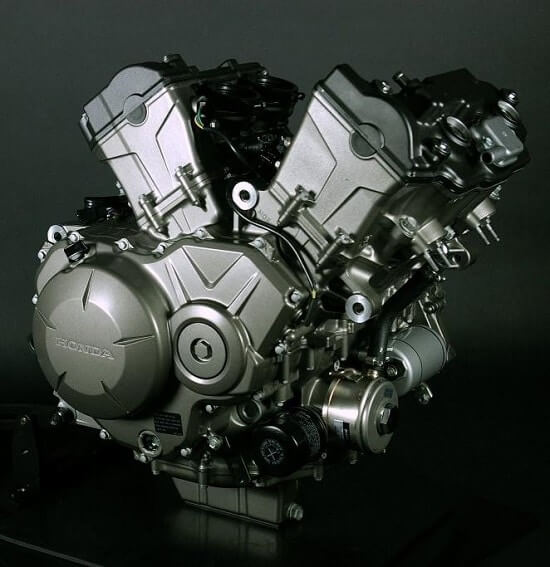
Motorcycle engines can have one to 6 cylinders. Usually, 4 cylinders are used for 600-1000cc motorcycles and twin cylinder is used in a variety of motorcycles.
For the past few years, the V-twin design has been the favourite choice of motorcycle engineers in Europe, America and Japan. The V-twin name comes from the V shape formation of 2-cylinders.
V-twin is just one type of engine designs, there are other ways to accommodate cylinders.’
Types of Twin-cylinder engines
- V-Twin
- Opposed-Twin
- Parallel-Twin
As we talked above, 4 cylinder engines are the most popular in the 600 to 1000cc segment, they run more smoothly when compared to other types of engines.
Types of 4-cylinder engines
- Inline 4 cylinder
- V-4
Transmission
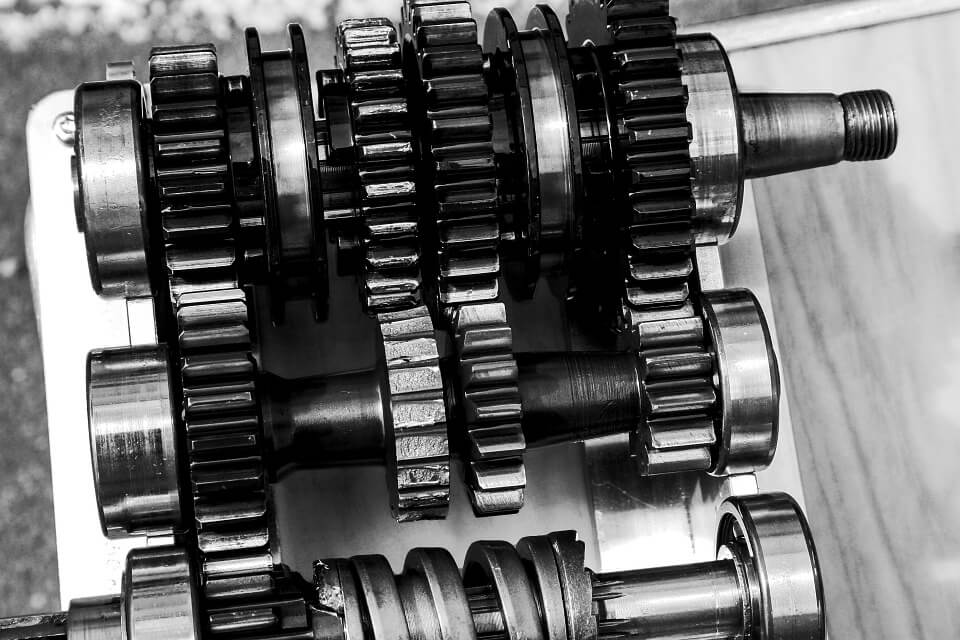

The energy generated by the engine is transmitted to the rear wheel of the motorcycle via transmission.
The transmission works with gears and clutch to deliver the power linearly to the rear wheel.
Also, Read How to Drift a Motorcycle



